2. Add Two Numbers
題目敘述
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order and each of their nodes contain a single digit. Add the two numbers and return it as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example 1:
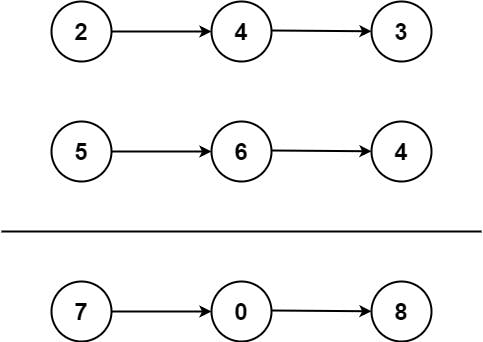
Input: l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
Output: [7,0,8]
Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807.
Example 2:
Input: l1 = [0], l2 = [0]
Output: [0]
Example 3:
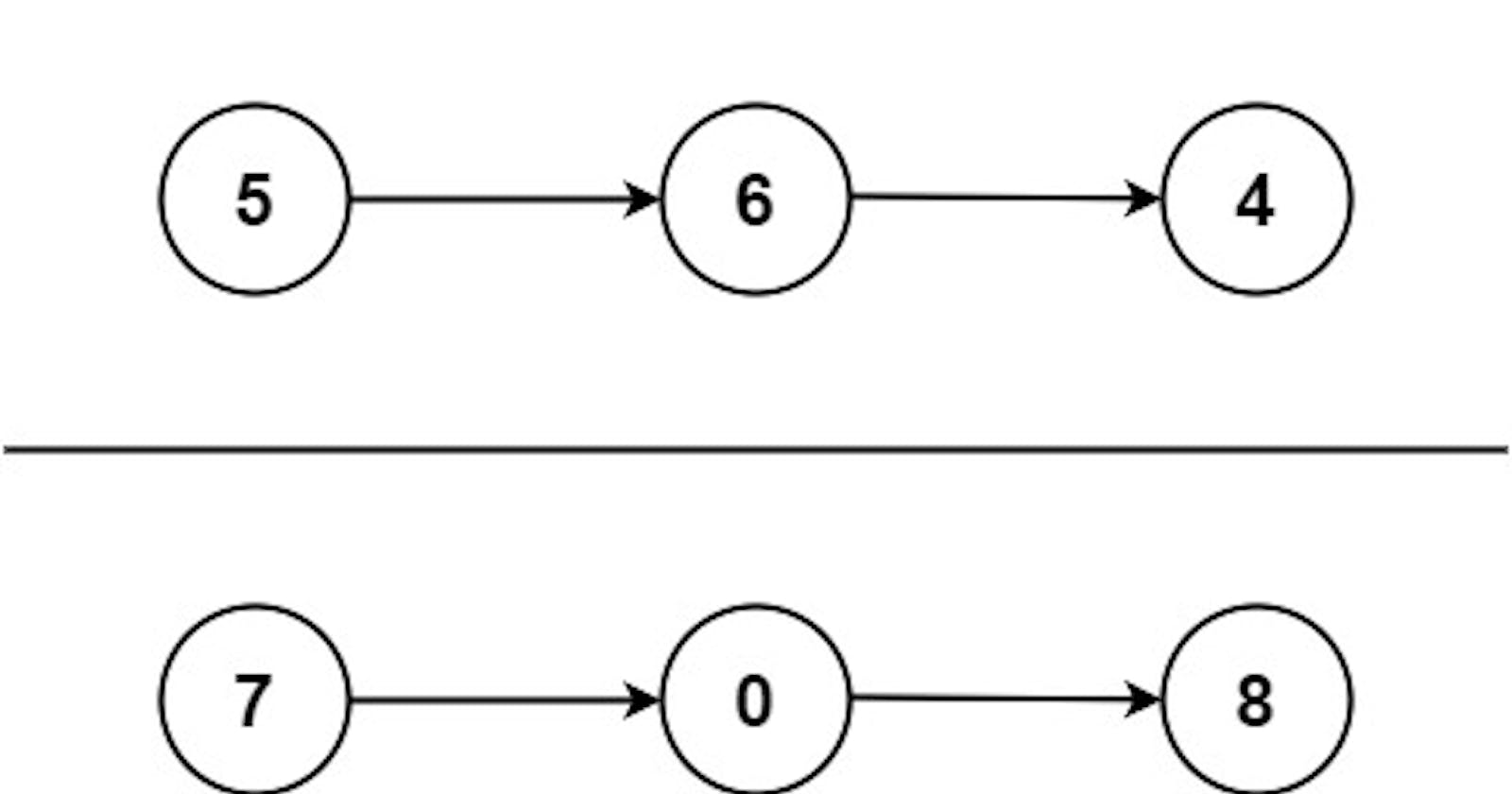
Input: l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9]
Output: [8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in each linked list is in the range
[1, 100]. 0 <= Node.val <= 9- It is guaranteed that the list represents a number that does not have leading zeros.
題目翻譯
給兩個資料結構為 Linked List 的參數 l1 和 l2,每個節點都只會有一個位數的值。要將兩個 list 相加。
解法解析
解題方式是最開始的個位數都是在最前面,所以其實很方便的就是從頭去開始遍歷來計算。當超過 10 就記住商數到參數 carry 帶到下個節點。
解法範例
Go
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func addTwoNumbers(l1 *ListNode, l2 *ListNode) *ListNode {
head := &ListNode{Val: 0}
n1, n2, carry, current := 0, 0, 0, head
for l1 != nil || l2 != nil || carry != 0 {
if l1 == nil {
n1 = 0
} else {
n1 = l1.Val
l1 = l1.Next
}
if l2 == nil {
n2 = 0
} else {
n2 = l2.Val
l2 = l2.Next
}
current.Next = &ListNode{Val: (n1 + n2 + carry) % 10}
current = current.Next
carry = (n1 + n2 + carry) / 10
}
return head.Next
}
JavaScript
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} l1
* @param {ListNode} l2
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var addTwoNumbers = function (l1, l2) {
const head = new ListNode(0);
let p = l1,
q = l2,
curr = head,
carry = 0;
while (p || q || carry) {
const x = p ? p.val : 0;
const y = q ? q.val : 0;
const sum = x + y + carry;
carry = Math.floor(sum / 10);
curr.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
curr = curr.next;
p = p ? p.next : null;
q = q ? q.next : null;
}
return head.next;
};
Kotlin
/**
* Example:
* var li = ListNode(5)
* var v = li.`val`
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode(var `val`: Int) {
* var next: ListNode? = null
* }
*/
class Solution {
fun addTwoNumbers(l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode): ListNode {
val result = ListNode(0)
var current = result
var l1Current: ListNode? = l1
var l2Current: ListNode? = l2
var carry = 0
while (l1Current != null || l2Current != null || carry > 0) {
val sum = (l1Current?.`val` ?: 0) + (l2Current?.`val` ?: 0) + carry
carry = sum / 10
val node = ListNode(sum % 10)
current?.next = node
current = node
l1Current = l1Current?.next
l2Current = l2Current?.next
}
return result.next
}
}
PHP
/**
* Definition for a singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* public $val = 0;
* public $next = null;
* function __construct($val = 0, $next = null) {
* $this->val = $val;
* $this->next = $next;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution
{
/**
* @param ListNode $l1
* @param ListNode $l2
* @return ListNode
*/
function addTwoNumbers($l1, $l2)
{
$dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
$p = $l1;
$q = $l2;
$curr = $dummyHead;
$carry = 0;
while ($p || $q || $carry) {
$x = $p ? $p->val : 0;
$y = $q ? $q->val : 0;
$sum = $x + $y + $carry;
$carry = intval($sum / 10);
$curr->next = new ListNode($sum % 10);
$curr = $curr->next;
$p = $p ? $p->next : null;
$q = $q ? $q->next : null;
}
return $dummyHead->next;
}
}
Python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: Optional[ListNode], l2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy_head = ListNode(0)
p = l1
q = l2
curr = dummy_head
carry = 0
while p or q or carry:
x = p.val if p else 0
y = q.val if q else 0
carry, remain = divmod(x + y + carry, 10)
curr.next = ListNode(remain)
curr = curr.next
p = p.next if p else None
q = q.next if q else None
return dummy_head.next
Rust
// Definition for singly-linked list.
// #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)]
// pub struct ListNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>>
// }
//
// impl ListNode {
// #[inline]
// fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// ListNode {
// next: None,
// val
// }
// }
// }
impl Solution {
pub fn add_two_numbers(l1: Option<Box<ListNode>>, l2: Option<Box<ListNode>>) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
let mut p = l1;
let mut q = l2;
let mut dummyHead = Some(Box::new(ListNode::new(0)));
let mut curr = dummyHead.as_mut();
let mut carry = 0;
while p.is_some() || q.is_some() || carry > 0{
let mut sum = carry;
if let Some(node) = p {
sum += node.val;
p = node.next;
}
if let Some(node) = q {
sum += node.val;
q = node.next;
}
if let Some(node) = curr {
node.next = Some(Box::new(ListNode::new(sum % 10)));
curr = node.next.as_mut();
}
carry = if sum >= 10 { 1 } else { 0 };
}
return dummyHead.unwrap().next;
}
}
Swift
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public var val: Int
* public var next: ListNode?
* public init(_ val: Int) {
* self.val = val
* self.next = nil
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
func addTwoNumbers(_ l1: ListNode?, _ l2: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
let dummyHead = ListNode( 0 )
var p = l1, q = l2, curr = dummyHead, carry = 0, r = 0, x = 0, y = 0, sum = 0
while p != nil || q != nil {
x = p?.val ?? 0
y = q?.val ?? 0
sum = x + y + carry
(carry,r) = sum.quotientAndRemainder(dividingBy: 10)
curr.next = ListNode( r )
curr = curr.next!
p = p?.next
q = q?.next
}
if ( carry > 0 ) {
curr.next = ListNode(1)
}
return dummyHead.next
}
}