498. Diagonal Traverse
題目敘述
Given an m x n matrix mat, return an array of all the elements of the array in a diagonal order.
Example 1:
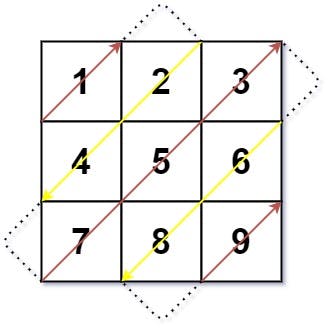
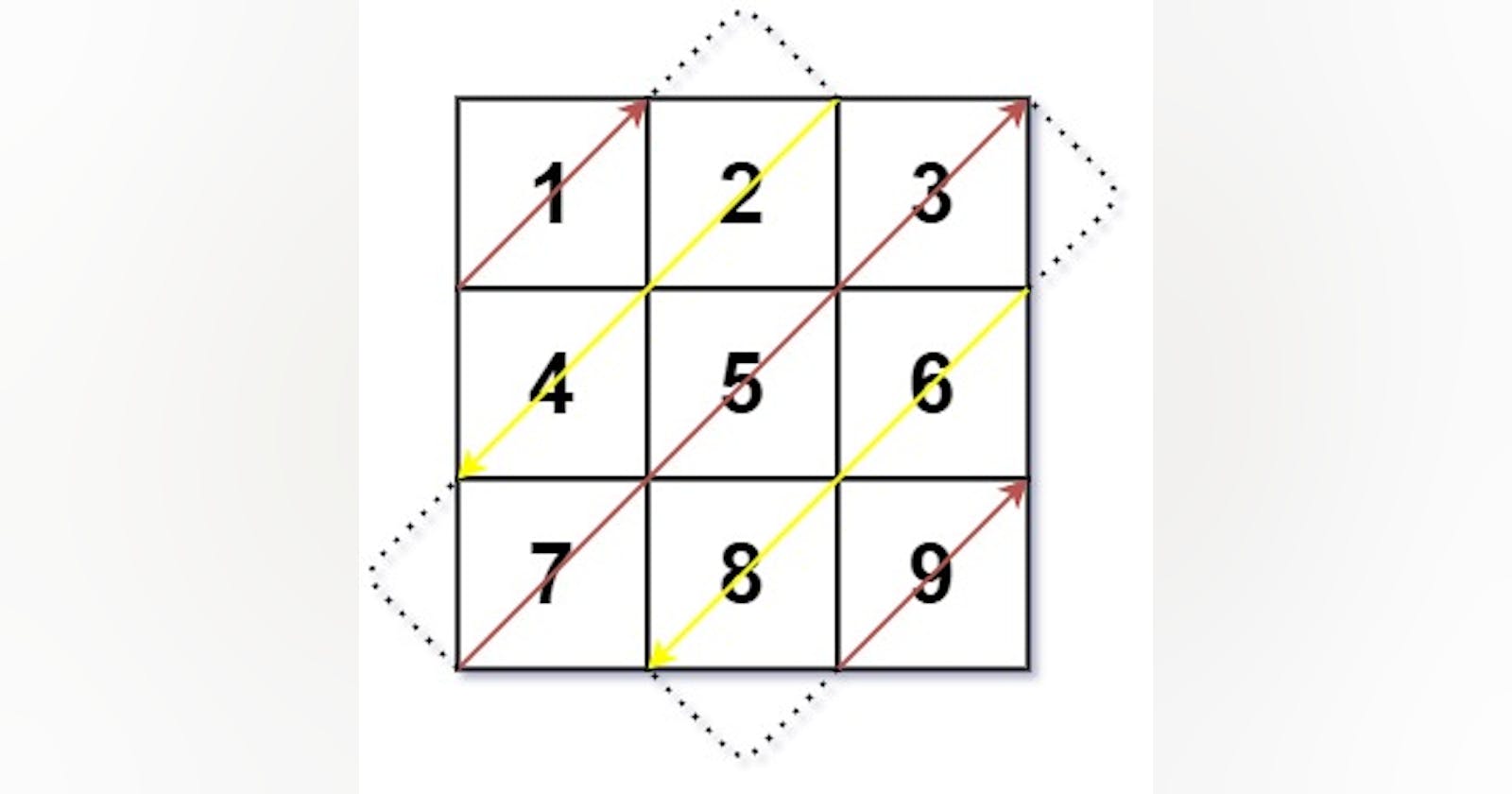
Input: mat = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
Output: [1,2,4,7,5,3,6,8,9]
Example 2:
Input: mat = [[1,2],[3,4]]
Output: [1,2,3,4]
Constraints:
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 10**41 <= m * n <= 10**4-10**5 <= mat[i][j] <= 10**5
題目翻譯
這題目是想要在一個二維陣列中,轉換成一個一維陣列。然後需要按照對角線 S 型的方式做排列順序。如範例一的圖示。
解法解析
這題官方給了兩種解法方式,基本概念還是主要計算 index 的方式。但是在討論區 tpt5cu 給出的解法,我覺得更簡單和好懂。
Diagonal Iteration and Reversal
這個解法是先從 row 行來遍歷(由左到右),到底後再換成 column 列來遍歷(由上到下)。每次移動時再來走對角線,其中在判斷是否為複數行來判斷是否需要做反轉方向。
Time:O(N⋅M)
Space:O(min(N, M))
Simulation
這個解法就滿麻煩的,是模擬對角線 S 型的方式來遍歷整個陣列。讓情況複雜許多,但是其空間複雜度是最低的,只有 O(1)
Time:O(N⋅M)
Space:O(1)
From discuss
這個解法就是從討論區來的,其概念很簡單,在同一個對角線的元素,其索引的相加都是相同的。例如 matrix[1][0] 和 matrix[0][1],的是在同一個對角線上,而且索引相加都是 1。所以很間單的對其相加的欄位放在一起,最後再依照複數行來判斷是否需要做反轉方向。
Time:O(N⋅M)
Space:O(N + M)
解法範例
Go
Diagonal Iteration and Reversal
func findDiagonalOrder(mat [][]int) []int {
var (
N int = len(mat)
M int = len(mat[0])
result []int
intermediate []int
)
for d := 0; d < N+M-1; d++ {
intermediate = []int{}
var r, c int
if d < M {
r, c = 0, d
} else {
r, c = d-M+1, M-1
}
for r < N && c >= 0 {
intermediate = append(intermediate, mat[r][c])
r++
c--
}
if d%2 == 0 {
for j := len(intermediate) - 1; j >= 0; j-- {
result = append(result, intermediate[j])
}
} else {
result = append(result, intermediate...)
}
}
return result
}
Simulation
func findDiagonalOrder(mat [][]int) []int {
var (
N int = len(mat)
M int = len(mat[0])
row int = 0
column int = 0
direction int = 1
result []int
)
for row < N && column < M {
result = append(result, mat[row][column])
var newRow, newColumn int
if direction == 1 {
newRow = row - 1
newColumn = column + 1
} else {
newRow = row + 1
newColumn = column - 1
}
if newRow < 0 || newRow >= N || newColumn < 0 || newColumn >= M {
if direction > 0 {
if column == M-1 {
row += 1
}
if column < M-1 {
column += 1
}
} else {
if row == N-1 {
column += 1
}
if row < N-1 {
row += 1
}
}
direction = 1 - direction
} else {
row = newRow
column = newColumn
}
}
return result
}
From discuss
func findDiagonalOrder(mat [][]int) []int {
d := [][]int{}
for i := 0; i < len(mat); i++ {
for j := 0; j < len(mat[i]); j++ {
if i+j < len(d) {
d[i+j] = append(d[i+j], mat[i][j])
} else {
d = append(d, []int{mat[i][j]})
}
}
}
result := []int{}
for idx, values := range d {
if idx%2 == 0 {
for j := len(values) - 1; j >= 0; j-- {
result = append(result, values[j])
}
} else {
result = append(result, values...)
}
}
return result
}
JavaScript
Diagonal Iteration and Reversal
/**
* @param {number[][]} mat
* @return {number[]}
*/
var findDiagonalOrder = function (mat) {
if (!mat || mat.length === 0) {
return [];
}
const N = mat.length,
M = mat[0].length,
result = [];
let intermediate = [];
for (let d = 0; d < N + M - 1; d++) {
intermediate = [];
let r = d - M + 1;
let c = M - 1;
if (d < M) {
r = 0;
c = d;
}
while (r < N && c >= 0) {
intermediate.push(mat[r][c]);
r++;
c--;
}
if (d % 2 === 0) {
intermediate = intermediate.reverse();
}
result.push(...intermediate);
}
return result;
};
Simulation
/**
* @param {number[][]} mat
* @return {number[]}
*/
var findDiagonalOrder = function (mat) {
if (!mat || mat.length === 0) {
return [];
}
const N = mat.length,
M = mat[0].length,
result = [];
let row = 0,
column = 0,
direction = 1;
while (row < N && column < M) {
result.push(mat[row][column]);
let newRow = row + (direction === 1 ? -1 : 1);
let newColumn = column + (direction === 1 ? 1 : -1);
if (newRow < 0 || newRow === N || newColumn < 0 || newColumn === M) {
if (direction) {
row += column === M - 1 ? 1 : 0;
column += column < M - 1 ? 1 : 0;
} else {
column += row === N - 1 ? 1 : 0;
row += row < N - 1 ? 1 : 0;
}
direction = 1 - direction;
} else {
row = newRow;
column = newColumn;
}
}
return result;
};
From discuss
/**
* @param {number[][]} mat
* @return {number[]}
*/
var findDiagonalOrder = function (mat) {
const d = {};
for (let i = 0; i < mat.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < mat[0].length; j++) {
d[i + j] = d[i + j] || [];
d[i + j].push(mat[i][j]);
}
}
const result = [];
for (const key in d) {
if (key % 2 === 0) {
result.push(...d[key].reverse());
} else {
result.push(...d[key]);
}
}
return result;
};
Kotlin
PHP
Diagonal Iteration and Reversal
class Solution
{
/**
* @param Integer[][] $mat
* @return Integer[]
*/
function findDiagonalOrder($mat)
{
$N = count($mat);
$M = count($mat[0]);
$result = array();
$intermediate = array();
for ($d = 0; $d < $N + $M - 1; $d++) {
$intermediate = array();
if ($d < $M) {
$r = 0;
$c = $d;
} else {
$r = $d - $M + 1;
$c = $M - 1;
}
while ($r < $N && $c >= 0) {
$intermediate[] = $mat[$r][$c];
$r++;
$c--;
}
if ($d % 2 == 0) {
$result = array_merge($result, array_reverse($intermediate));
} else {
$result = array_merge($result, $intermediate);
}
}
return $result;
}
}
Simulation
class Solution
{
/**
* @param Integer[][] $mat
* @return Integer[]
*/
function findDiagonalOrder($mat)
{
$m = count($mat);
$n = count($mat[0]);
$r = $c = 0;
for ($i = 0; $i < $m * $n; $i++) {
$ans[] = $mat[$r][$c];
if (($r + $c) % 2 == 0) {
if ($c == $n - 1) {
$r++;
} elseif ($r == 0) {
$c++;
} else {
$r--;
$c++;
}
} else {
if ($r == $m - 1) {
$c++;
} elseif ($c == 0) {
$r++;
} else {
$r++;
$c--;
}
}
}
return $ans;
}
}
From discuss
class Solution
{
/**
* @param Integer[][] $mat
* @return Integer[]
*/
function findDiagonalOrder($mat)
{
$d = array();
for ($i = 0; $i < count($mat); $i++) {
for ($j = 0; $j < count($mat[$i]); $j++) {
if (!isset($d[$i + $j])) {
$d[$i + $j] = array();
}
$d[$i + $j][] = $mat[$i][$j];
}
}
$result = array();
foreach ($d as $key => $value) {
if ($key % 2 == 0) {
$result = array_merge($result, array_reverse($value));
} else {
$result = array_merge($result, $value);
}
}
return $result;
}
}
Python
Diagonal Iteration and Reversal
class Solution:
def findDiagonalOrder(self, mat: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
# Check for empty matrices
if not mat or not mat[0]:
return []
# Variables to track the size of the matrix
N, M = len(mat), len(mat[0])
# The two arrays as explained in the algorithm
result, intermediate = [], []
# We have to go over all the elements in the first
# row and the last column to cover all possible diagonals
for d in range(N + M - 1):
# Clear the intermediate array everytime we start
# to process another diagonal
intermediate.clear()
# We need to figure out the "head" of this diagonal
# The elements in the first row and the last column
# are the respective heads.
if d < M:
r, c = 0, d
else:
r, c = d - M + 1, M - 1
# Iterate until one of the indices goes out of scope
# Take note of the index math to go down the diagonal
while r < N and c > -1:
intermediate.append(mat[r][c])
r += 1
c -= 1
# Reverse even numbered diagonals. The
# article says we have to reverse odd
# numbered articles but here, the numbering
# is starting from 0 :P
if d % 2 == 0:
result.extend(intermediate[::-1])
else:
result.extend(intermediate)
return result
Simulation
class Solution:
def findDiagonalOrder(self, mat: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
# Check for an empty matrix
if not mat or not mat[0]:
return []
# The dimensions of the matrix
N, M = len(mat), len(mat[0])
# Incides that will help us progress through
# the matrix, one element at a time.
row, column = 0, 0
# As explained in the article, this is the variable
# that helps us keep track of what direction we are
# processing the current diaonal
direction = 1
# Final result array that will contain all the elements
# of the matrix
result = []
# The uber while loop which will help us iterate over all
# the elements in the array.
while row < N and column < M:
# First and foremost, add the current element to
# the result matrix.
result.append(mat[row][column])
# Move along in the current diagonal depending upon
# the current direction.[i, j] -> [i - 1, j + 1] if
# going up and [i, j] -> [i + 1][j - 1] if going down.
new_row = row + (-1 if direction == 1 else 1)
new_column = column + (1 if direction == 1 else -1)
# Checking if the next element in the diagonal is within the
# bounds of the matrix or not. If it's not within the bounds,
# we have to find the next head.
if new_row < 0 or new_row == N or new_column < 0 or new_column == M:
# If the current diagonal was going in the upwards
# direction.
if direction:
# For an upwards going diagonal having [i, j] as its tail
# If [i, j + 1] is within bounds, then it becomes
# the next head. Otherwise, the element directly below
# i.e. the element [i + 1, j] becomes the next head
row += (column == M - 1)
column += (column < M - 1)
else:
# For a downwards going diagonal having [i, j] as its tail
# if [i + 1, j] is within bounds, then it becomes
# the next head. Otherwise, the element directly below
# i.e. the element [i, j + 1] becomes the next head
column += (row == N - 1)
row += (row < N - 1)
# Flip the direction
direction = 1 - direction
else:
row = new_row
column = new_column
return result
From discuss
class Solution(object):
def findDiagonalOrder(self, mat: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
"""
:type mat: List[List[int]]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
d = {}
# loop through matrix
for i in range(len(mat)):
for j in range(len(mat[i])):
# if no entry in dictionary for sum of indices aka the diagonal, create one
if i + j not in d:
d[i + j] = []
# If you've already passed over this diagonal, keep adding elements to it!
d[i + j].append(mat[i][j])
# we're done with the pass, let's build our answer array
ans = []
# look at the diagonal and each diagonal's elements
for entry in d.items():
# each entry looks like (diagonal level (sum of indices), [elem1, elem2, elem3, ...])
# snake time, look at the diagonal level
if entry[0] % 2 == 0:
# Here we append in reverse order because its an even numbered level/diagonal.
ans.extend(entry[1][::-1])
else:
ans.extend(entry[1])
return ans
Rust
Swift