538. Convert BST to Greater Tree
題目敘述
Given the root of a Binary Search Tree (BST), convert it to a Greater Tree such that every key of the original BST is changed to the original key plus the sum of all keys greater than the original key in BST.
As a reminder, a binary search tree is a tree that satisfies these constraints:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node's key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Example 1:
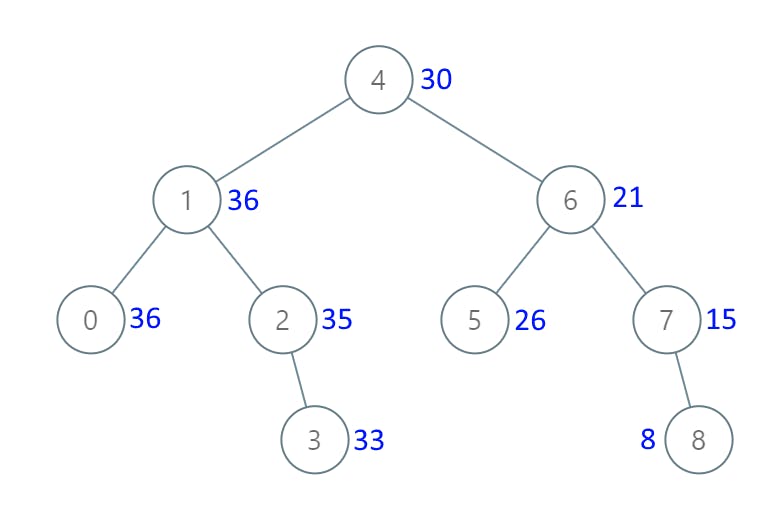
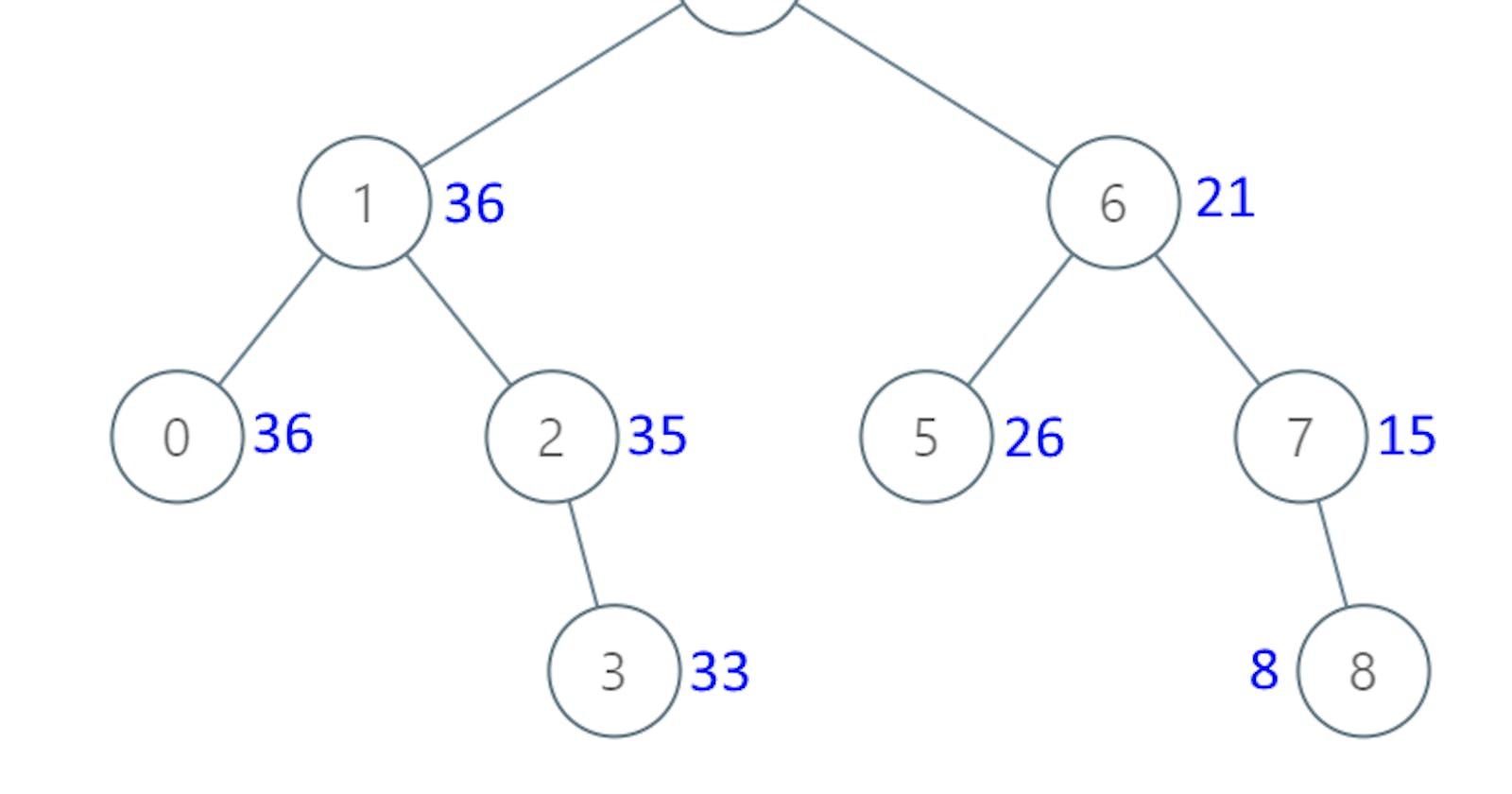
Input: root = [4,1,6,0,2,5,7,null,null,null,3,null,null,null,8]
Output: [30,36,21,36,35,26,15,null,null,null,33,null,null,null,8]
Example 2:
Input: root = [0,null,1]
Output: [1,null,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 10**4]. 10**4 <= Node.val <= 10**4- All the values in the tree are unique.
rootis guaranteed to be a valid binary search tree.
Note: This question is the same as 1038: https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-search-tree-to-greater-sum-tree/
題目翻譯
這題會給一個二元搜尋樹,然後要從大到小依序的累加。可以看範例一的圖,從 8 一路的累加到 0。
解法解析
這題的解法官方有三種,Recursion、Iteration with a Stack、Morris In-order Traversal。前面兩種時間複雜度跟空間複雜度都一樣是 O(n)。最後一個演算法,可以達到空間複雜度只有 O(1)。但我要吐槽一下,結果我每個程式解答送出後,都是前兩個在前面,有時候真的演算法看看就好,真的還是跑起來才知道呢。
Recursion
這是滿簡單的思維,就是我們用反序的方式遍歷整個二元搜尋樹,然後紀錄每一次的加總並更新節點的值。
Iteration with a Stack
有點算是從 Recursion 而來的想法,首先初始化一個空的 Stack 並把 root 作為當前節點。跟 Recursion 不同的是,我們是透過 Stack 來記住上一個節點。
Morris In-order Traversal
- 當節點的右節點為空,代表沒有更大的值,所以處理加總當前節點後去遍歷左節點
- 當節點的右節點不為空,代表還有更大的值。找出右節點的最左節點(因為會是當前排序的下一個節點)
- 當左節點的不存在,則將其指向當前節點( 代表說反序時,下一個值是目前的節點)
- 當左節點存在且跟當前節點不同(因為有可能是上面步驟增加的連結),則將其左節點社為空,並處理當前結點
解法範例
Go
Recursion
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func convertBST(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
total := 0
var convert func(*TreeNode)
convert = func(node *TreeNode) {
if node != nil {
convert(node.Right)
total += node.Val
node.Val = total
convert(node.Left)
}
}
convert(root)
return root
}
Iteration
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func convertBST(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
total := 0
node := root
stack := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
for node != nil || len(stack) > 0 {
for node != nil {
stack = append(stack, node)
node = node.Right
}
node = stack[len(stack)-1]
stack = stack[:len(stack)-1]
total += node.Val
node.Val = total
node = node.Left
}
return root
}
Morris Traversal
func getSuccessor(node *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
succ := node.Right
for succ.Left != nil && succ.Left != node {
succ = succ.Left
}
return succ
}
func convertBST(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
total := 0
node := root
for node != nil {
if node.Right == nil {
total += node.Val
node.Val = total
node = node.Left
} else {
succ := getSuccessor(node)
if succ.Left == nil {
succ.Left = node
node = node.Right
} else {
succ.Left = nil
total += node.Val
node.Val = total
node = node.Left
}
}
}
return root
}
JavaScript
Recursion
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var convertBST = function (root) {
let total = 0;
convert(root);
function convert(root) {
if (!root) return;
convert(root.right);
total += root.val;
root.val = total;
convert(root.left);
}
return root;
};
Iteration
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var convertBST = function (root) {
let total = 0,
node = root;
const stack = [];
while (node || stack.length) {
while (node) {
stack.push(node);
node = node.right;
}
node = stack.pop();
total += node.val;
node.val = total;
node = node.left;
}
return root;
};
Morris Traversal
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var convertBST = function (root) {
let total = 0,
node = root;
while (node) {
if (!node.right) {
total += node.val;
node.val = total;
node = node.left;
} else {
const succ = getSuccessor(node);
if (succ.left) {
succ.left = null;
total += node.val;
node.val = total;
node = node.left;
} else {
succ.left = node;
node = node.right;
}
}
}
return root;
};
const getSuccessor = (node) => {
let succ = node.right;
while (succ.left && succ.left !== node) {
succ = succ.left;
}
return succ;
};
Kotlin
PHP
Python
Recursion
class Solution(object):
def __init__(self):
self.total = 0
def convertBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if root is not None:
self.convertBST(root.right)
self.total += root.val
root.val = self.total
self.convertBST(root.left)
return root
Iteration
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def convertBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
total = 0
node = root
stack: List[TreeNode] = []
while stack or node is not None:
# push all nodes up to (and including) this subtree's maximum on
# the stack.
while node is not None:
stack.append(node)
node = node.right
node = stack.pop()
total += node.val
node.val = total
# all nodes with values between the current and its parent lie in
# the left subtree.
node = node.left
return root
Morris Traversal
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def convertBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
# Get the node with the smallest value greater than this one.
def get_successor(node):
succ = node.right
while succ.left is not None and succ.left is not node:
succ = succ.left
return succ
total = 0
node = root
while node is not None:
# If there is no right subtree, then we can visit this node and
# continue traversing left.
if node.right is None:
total += node.val
node.val = total
node = node.left
# If there is a right subtree, then there is a node that has a
# greater value than the current one. therefore, we must traverse
# that node first.
else:
succ = get_successor(node)
# If there is no left subtree (or right subtree, because we are
# in this branch of control flow), make a temporary connection
# back to the current node.
if succ.left is None:
succ.left = node
node = node.right
# If there is a left subtree, it is a link that we created on
# a previous pass, so we should unlink it and visit this node.
else:
succ.left = None
total += node.val
node.val = total
node = node.left
return root
Rust
Swift