669. Trim a Binary Search Tree
題目敘述
Given the root of a binary search tree and the lowest and highest boundaries as low and high, trim the tree so that all its elements lies in [low, high]. Trimming the tree should not change the relative structure of the elements that will remain in the tree (i.e., any node's descendant should remain a descendant). It can be proven that there is a unique answer.
Return the root of the trimmed binary search tree. Note that the root may change depending on the given bounds.
Example 1:
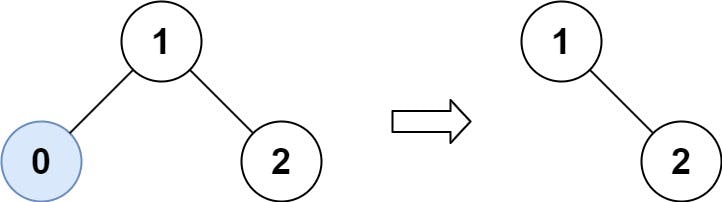
Input: root = [1,0,2], low = 1, high = 2
Output: [1,null,2]
Example 2:
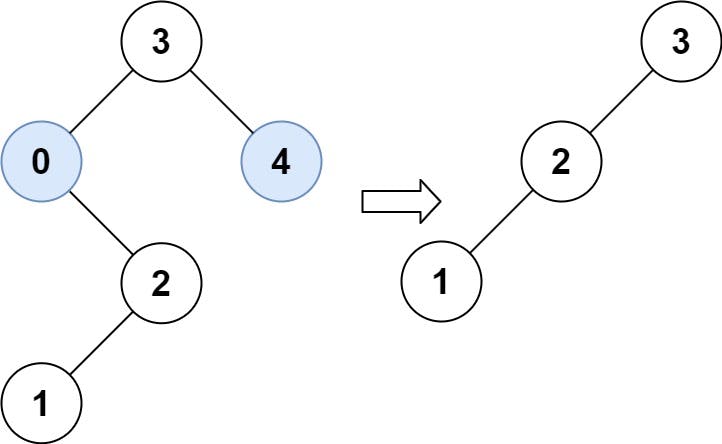
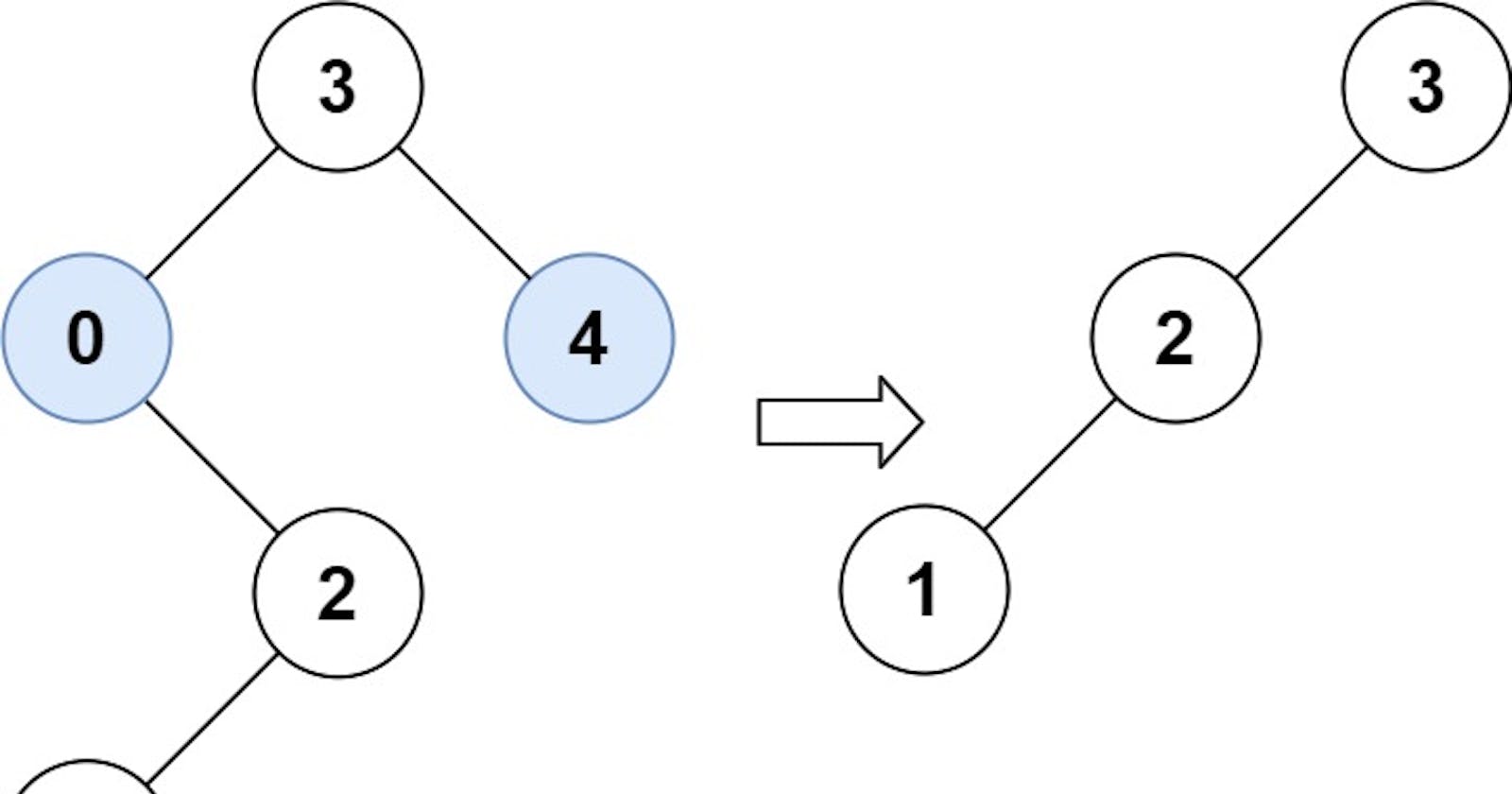
Input: root = [3,0,4,null,2,null,null,1], low = 1, high = 3
Output: [3,2,null,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree in the range
[1, 104]. 0 <= Node.val <= 10**4- The value of each node in the tree is unique.
rootis guaranteed to be a valid binary search tree.0 <= low <= high <= 10**4
題目翻譯
題目的需求很簡單,就是有一個二元搜尋樹 root。然後我們需要去修剪其中的節點,修剪的條件會有兩個參數 low 和 high,只要節點的值不在這個範圍內就會被刪減掉。
解法解析
這題的解法就是使用了遞迴,去搜尋全部的節點。對每個節點判斷其範圍後去覆蓋前一個節點的位置。
解法範例
Go
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func trimBST(root *TreeNode, low int, high int) *TreeNode {
if root == nil {
return nil
} else if root.Val < low {
return trimBST(root.Right, low, high)
} else if root.Val > high {
return trimBST(root.Left, low, high)
}
root.Left = trimBST(root.Left, low, high)
root.Right = trimBST(root.Right, low, high)
return root
}
JavaScript
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} low
* @param {number} high
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var trimBST = function (root, low, high) {
if (!root) return null;
if (root.val < low) return trimBST(root.right, low, high);
if (root.val > high) return trimBST(root.left, low, high);
root.left = trimBST(root.left, low, high);
root.right = trimBST(root.right, low, high);
return root;
};
Kotlin
這邊是利用 Kotlin 可以將判斷式當作一個 return 的方式
/**
* Example:
* var ti = TreeNode(5)
* var v = ti.`val`
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode(var `val`: Int) {
* var left: TreeNode? = null
* var right: TreeNode? = null
* }
*/
class Solution {
fun trimBST(root: TreeNode?, low: Int, high: Int): TreeNode? {
return if (root == null) {
null
} else if (root.`val` < low) {
trimBST(root.right, low, high)
} else if (root.`val` > high) {
trimBST(root.left, low, high)
} else {
root.left = trimBST(root.left, low, high)
root.right = trimBST(root.right, low, high)
root
}
}
}
PHP
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* public $val = null;
* public $left = null;
* public $right = null;
* function __construct($val = 0, $left = null, $right = null) {
* $this->val = $val;
* $this->left = $left;
* $this->right = $right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution
{
/**
* @param TreeNode $root
* @param Integer $low
* @param Integer $high
* @return TreeNode
*/
function trimBST($root, $low, $high)
{
if ($root == null) {
return null;
}
if ($root->val < $low) {
return $this->trimBST($root->right, $low, $high);
}
if ($root->val > $high) {
return $this->trimBST($root->left, $low, $high);
}
$root->left = $this->trimBST($root->left, $low, $high);
$root->right = $this->trimBST($root->right, $low, $high);
return $root;
}
}
Python
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def trimBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], low: int, high: int) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
def trim(node):
if node is None:
return node
elif node.val > high:
return trim(node.left)
elif node.val < low:
return trim(node.right)
else:
node.left = trim(node.left)
node.right = trim(node.right)
return node
return trim(root)
Rust
// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
impl Solution {
pub fn trim_bst(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, low: i32, high: i32) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
if let Some(node_ref) = root {
let mut node = node_ref.borrow_mut();
if node.val > high {
return Self::trim_bst(node.left.clone(), low, high);
} else if node.val < low {
return Self::trim_bst(node.right.clone(), low, high);
}
node.left = Self::trim_bst(node.left.clone(), low, high);
node.right = Self::trim_bst(node.right.clone(), low, high);
Some(node_ref.clone())
} else {
None
}
}
}
Swift
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* public var val: Int
* public var left: TreeNode?
* public var right: TreeNode?
* public init() { self.val = 0; self.left = nil; self.right = nil; }
* public init(_ val: Int) { self.val = val; self.left = nil; self.right = nil; }
* public init(_ val: Int, _ left: TreeNode?, _ right: TreeNode?) {
* self.val = val
* self.left = left
* self.right = right
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
func trimBST(_ root: TreeNode?, _ low: Int, _ high: Int) -> TreeNode? {
guard let root = root else {
return nil
}
if root.val < low {
return trimBST(root.right, low, high)
}
if root.val > high {
return trimBST(root.left, low, high)
}
root.left = trimBST(root.left, low, high)
root.right = trimBST(root.right, low, high)
return root
}
}