160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists
題目敘述
Given the heads of two singly linked-lists headA and headB, return the node at which the two lists intersect. If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return null.
For example, the following two linked lists begin to intersect at node c1:
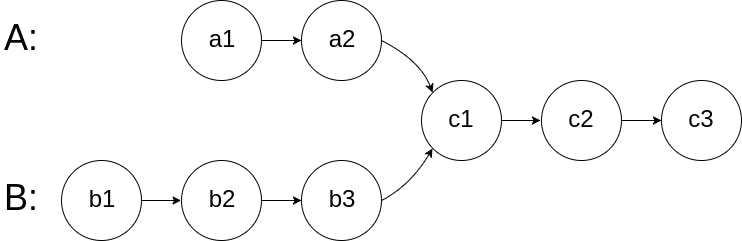
The test cases are generated such that there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
Note that the linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
Custom Judge:
The inputs to the judge are given as follows (your program is not given these inputs):
intersectVal- The value of the node where the intersection occurs. This is0if there is no intersected node.listA- The first linked list.listB- The second linked list.skipA- The number of nodes to skip ahead inlistA(starting from the head) to get to the intersected node.skipB- The number of nodes to skip ahead inlistB(starting from the head) to get to the intersected node.
The judge will then create the linked structure based on these inputs and pass the two heads, headA and headB to your program. If you correctly return the intersected node, then your solution will be accepted.
Example 1:
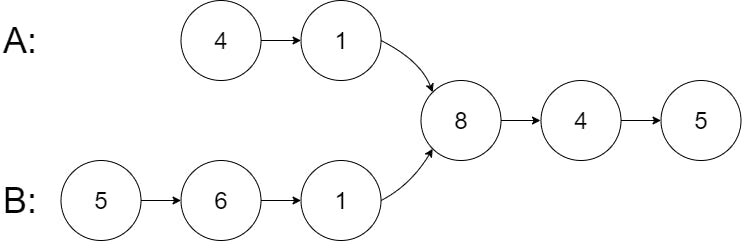
Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
Output: Intersected at '8'
Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect).
From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,6,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.
Example 2:
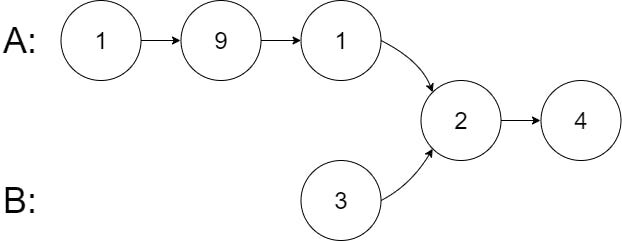
Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [1,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
Output: Intersected at '2'
Explanation: The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect).
From the head of A, it reads as [1,9,1,2,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.
Example 3:
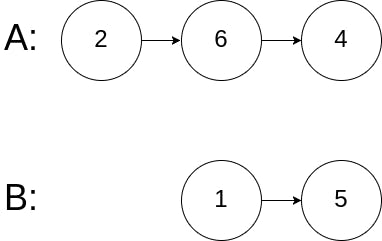
Input: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
Output: No intersection
Explanation: From the head of A, it reads as [2,6,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [1,5]. Since the two lists do not intersect, intersectVal must be 0, while skipA and skipB can be arbitrary values.
Explanation: The two lists do not intersect, so return null.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes of
listAis in them. - The number of nodes of
listBis in then. 1 <= m, n <= 3 * 10**41 <= Node.val <= 10**50 <= skipA < m0 <= skipB < nintersectValis0iflistAandlistBdo not intersect.intersectVal == listA[skipA] == listB[skipB]iflistAandlistBintersect.
Follow up: Could you write a solution that runs in O(m + n) time and use only O(1) memory?
題目翻譯
題目很間單的需求,就是有兩個連結序列 A 和 B,找出兩個序列是不是有交會的節點。如果有就回傳該交匯點,如果沒有的話就回傳 null。
解法解析
主要有三種解法,第一種就是直接的暴力解,用雙層迴圈去比對。第二種就是犧牲一些空間,使用 Hash Table 的方式去紀錄已經走過的節點去比對。第三種則是使用 Two Pointer 的方式。
Two pointer
此解法滿巧妙的,真的一開始沒想到。因為 A 和 B 如果有交會點的話,代表說從這個交會點開始的長度都是一樣的,定義這交會點之後的為 C。
A = a + C
B = b + C
這種情況的話就是 a 和 b 之間的長度差距了,而這簡單的方式就是當 A 和 B 走完後,會到另一個序列來走,相當於以下的結果:
Pointer A:(a + C) + (b + C)
Pointer B:(b + C) + (a + C)
在這種情況下,兩個 Pointer 走完的程度是一樣的,所以就會最後在交會點碰面。
解法範例
Go
Brute force
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func getIntersectionNode(headA, headB *ListNode) *ListNode {
for headA != nil {
var pB *ListNode = headB
for pB != nil {
if headA == pB {
return headA
}
pB = pB.Next
}
headA = headA.Next
}
return nil
}
Hash table
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func getIntersectionNode(headA, headB *ListNode) *ListNode {
var nodesInB = make(map[*ListNode]bool)
for headB != nil {
nodesInB[headB] = true
headB = headB.Next
}
for headA != nil {
if nodesInB[headA] {
return headA
}
headA = headA.Next
}
return nil
}
Two pointer
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func getIntersectionNode(headA, headB *ListNode) *ListNode {
var pA, pB *ListNode = headA, headB
for pA != pB {
if pA == nil {
pA = headB
} else {
pA = pA.Next
}
if pB == nil {
pB = headA
} else {
pB = pB.Next
}
}
return pA
}
JavaScript
Brute force
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} headA
* @param {ListNode} headB
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var getIntersectionNode = function (headA, headB) {
while (headA) {
let pB = headB;
while (pB) {
if (headA === pB) {
return headA;
}
pB = pB.next;
}
headA = headA.next;
}
return null;
};
Hash table
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} headA
* @param {ListNode} headB
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var getIntersectionNode = function (headA, headB) {
const nodesInB = new Set();
while (headB) {
nodesInB.add(headB);
headB = headB.next;
}
while (headA) {
if (nodesInB.has(headA)) {
return headA;
}
headA = headA.next;
}
return null;
};
Two pointer
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} headA
* @param {ListNode} headB
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var getIntersectionNode = function (headA, headB) {
let pA = headA;
let pB = headB;
while (pA !== pB) {
pA = pA ? pA.next : headB;
pB = pB ? pB.next : headA;
}
return pA;
};
Kotlin
Brute force
/**
* Example:
* var li = ListNode(5)
* var v = li.`val`
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode(var `val`: Int) {
* var next: ListNode? = null
* }
*/
class Solution {
fun getIntersectionNode(headA:ListNode?, headB:ListNode?):ListNode? {
var pA: ListNode? = headA
while (pA != null) {
var pB: ListNode? = headB
while (pB != null) {
if (pB == pA) {
return pA
}
pB = pB.next
}
pA = pA.next
}
return null
}
}
Hash table
/**
* Example:
* var li = ListNode(5)
* var v = li.`val`
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode(var `val`: Int) {
* var next: ListNode? = null
* }
*/
class Solution {
fun getIntersectionNode(headA:ListNode?, headB:ListNode?):ListNode? {
var nodesInB = HashSet<ListNode>()
var node: ListNode? = headB
while (node != null) {
nodesInB.add(node)
node = node.next
}
node = headA
while (node != null) {
if (nodesInB.contains(node)) {
return node
}
node = node.next
}
return null
}
}
Two pointer
/**
* Example:
* var li = ListNode(5)
* var v = li.`val`
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode(var `val`: Int) {
* var next: ListNode? = null
* }
*/
class Solution {
fun getIntersectionNode(headA:ListNode?, headB:ListNode?):ListNode? {
var pA: ListNode? = headA
var pB: ListNode? = headB
while (pA != pB) {
pA = if (pA == null) headB else pA.next
pB = if (pB == null) headA else pB.next
}
return pA
}
}
PHP
Brute force
/**
* Definition for a singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* public $val = 0;
* public $next = null;
* function __construct($val) { $this->val = $val; }
* }
*/
class Solution
{
/**
* @param ListNode $headA
* @param ListNode $headB
* @return ListNode
*/
function getIntersectionNode($headA, $headB)
{
while ($headA) {
$pB = $headB;
while ($pB) {
if ($pB === $headA) {
return $headA;
}
$pB = $pB->next;
}
$headA = $headA->next;
}
return null;
}
}
Hash table
/**
* Definition for a singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* public $val = 0;
* public $next = null;
* function __construct($val) { $this->val = $val; }
* }
*/
class Solution
{
/**
* @param ListNode $headA
* @param ListNode $headB
* @return ListNode
*/
function getIntersectionNode($headA, $headB)
{
$nodesInB = [];
while ($headB) {
$nodesInB[spl_object_id($headB)] = true;
$headB = $headB->next;
}
while ($headA) {
if (isset($nodesInB[spl_object_id($headA)])) {
return $headA;
}
$headA = $headA->next;
}
return null;
}
}
Two pointer
/**
* Definition for a singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* public $val = 0;
* public $next = null;
* function __construct($val) { $this->val = $val; }
* }
*/
class Solution
{
/**
* @param ListNode $headA
* @param ListNode $headB
* @return ListNode
*/
function getIntersectionNode($headA, $headB)
{
$pA = $headA;
$pB = $headB;
while ($pA !== $pB) {
$pA = $pA ? $pA->next : $headB;
$pB = $pB ? $pB->next : $headA;
}
return $pA;
}
}
Python
Brute force
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(
self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode
) -> Optional[ListNode]:
while headA:
pB = headB
while pB:
if headA == pB:
return headA
pB = pB.next
headA = headA.next
return None
Hash table
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(
self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode
) -> Optional[ListNode]:
nodes_in_B = set()
while headB:
nodes_in_B.add(headB)
headB = headB.next
while headA:
if headA in nodes_in_B:
return headA
headA = headA.next
return None
Two pointer
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(
self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode
) -> Optional[ListNode]:
pA = headA
pB = headB
while pA != pB:
pA = pA.next if pA else headB
pB = pB.next if pB else headA
return pA
Rust
Swift
Brute force
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public var val: Int
* public var next: ListNode?
* public init(_ val: Int) {
* self.val = val
* self.next = nil
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
func getIntersectionNode(_ headA: ListNode?, _ headB: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
var a = headA
while a != nil {
var pB = headB
while pB != nil{
if a === pB {
return a
}
pB = pB?.next
}
a = a?.next
}
return nil
}
}
Hash table
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public var val: Int
* public var next: ListNode?
* public init(_ val: Int) {
* self.val = val
* self.next = nil
* }
* }
*/
extension ListNode: Equatable, Hashable {
public static func == (lhs: ListNode, rhs: ListNode) -> Bool {
return lhs === rhs
}
public func hash(into hasher: inout Hasher) {
hasher.combine(val + (next?.val ?? 0))
}
}
class Solution {
func getIntersectionNode(_ headA: ListNode?, _ headB: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
var nodesInB = Set<ListNode>()
var temp = headB
while temp != nil {
nodesInB.insert(temp!)
temp = temp?.next
}
temp = headA
while temp != nil {
if nodesInB.contains(temp!) {
return temp
}
temp = temp?.next
}
return nil
}
}
Two pointer
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public var val: Int
* public var next: ListNode?
* public init(_ val: Int) {
* self.val = val
* self.next = nil
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
func getIntersectionNode(_ headA: ListNode?, _ headB: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
var pA: ListNode? = headA
var pB: ListNode? = headB
while pA !== pB {
pA = pA == nil ? headB : pA?.next
pB = pB == nil ? headA : pB?.next
}
return pA
}
}
