142. Linked List Cycle II
題目敘述
Given the head of a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
There is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list that can be reached again by continuously following the next pointer. Internally, pos is used to denote the index of the node that tail's next pointer is connected to (0-indexed). It is -1 if there is no cycle. Note that pos is not passed as a parameter.
Do not modify the linked list.
Example 1:
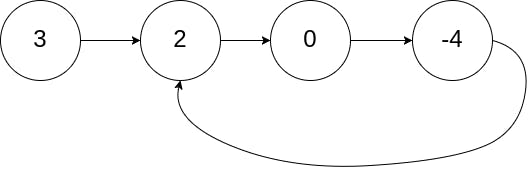
Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
Output: tail connects to node index 1
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the second node.
Example 2:
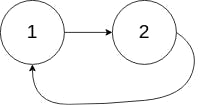
Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
Output: tail connects to node index 0
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the first node.
Example 3:

Input: head = [1], pos = -1
Output: no cycle
Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.
Constraints:
- The number of the nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 10**4]. -10**5 <= Node.val <= 10**5posis-1or a valid index in the linked-list.
Follow up: Can you solve it using O(1) (i.e. constant) memory?
題目翻譯
嘗試在空間複雜度是常數的情況下解題。
這題是昨天 141 的延伸,有一個連接序列 head,要找出迴圈開始的節點。如果沒有迴圈就回傳 null。
解法解析
解法也是跟昨天的 141 一樣,使用 Hash Table 或是判圈演算法。不同的是因為要找出的是迴圈的連接點,所以在找到龜兔的交會點時,會需要再從交會點和起始點,重新做一次同速比較來找出迴圈的連接點。詳細的解法概念,應該會再另外寫在演算法系列吧。
解法範例
Go
Hash Table
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func detectCycle(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
var visited = make(map[*ListNode]bool)
node := head
for node != nil {
if visited[node] {
return node
}
visited[node] = true
node = node.Next
}
return nil
}
Floyd's Tortoise and Hare
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func detectCycle(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
if head == nil {
return nil
}
intersect := getIntersect(head)
if intersect == nil {
return nil
}
ptr1 := head
ptr2 := intersect
for ptr1 != ptr2 {
ptr1 = ptr1.Next
ptr2 = ptr2.Next
}
return ptr1
}
func getIntersect(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
tortoise := head
hare := head
for hare != nil && hare.Next != nil {
tortoise = tortoise.Next
hare = hare.Next.Next
if hare == tortoise {
return tortoise
}
}
return nil
}
JavaScript
Hash Table
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var detectCycle = function (head) {
const visited = new Set();
let node = head;
while (node !== null) {
if (visited.has(node)) {
return node;
}
visited.add(node);
node = node.next;
}
return null;
};
Floyd's Tortoise and Hare
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var detectCycle = function (head) {
if (head === null) return null;
const intersection = getIntersection(head);
if (intersection === null) return null;
let ptr1 = head,
ptr2 = intersection;
while (ptr1 !== ptr2) {
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
ptr1 = ptr1.next;
}
return ptr1;
};
const getIntersection = (head) => {
let tortoise = head,
hare = head;
while (hare !== null && hare.next !== null) {
tortoise = tortoise.next;
hare = hare.next.next;
if (tortoise === hare) return tortoise;
}
return null;
};
Kotlin
Hash Table
/**
* Example:
* var li = ListNode(5)
* var v = li.`val`
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode(var `val`: Int) {
* var next: ListNode? = null
* }
*/
class Solution {
fun detectCycle(head: ListNode?): ListNode? {
val visited = mutableSetOf<ListNode>()
var node = head
while (node != null) {
if (visited.contains(node)) {
return node
}
visited.add(node)
node = node.next
}
return null
}
}
Floyd's Tortoise and Hare
/**
* Example:
* var li = ListNode(5)
* var v = li.`val`
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode(var `val`: Int) {
* var next: ListNode? = null
* }
*/
class Solution {
private fun getIntersect(head: ListNode): ListNode? {
var tortoise: ListNode? = head
var hare: ListNode? = head
// A fast pointer will either loop around a cycle and meet the slow
// pointer or reach the `null` at the end of a non-cyclic list.
while (hare != null && hare.next != null) {
tortoise = tortoise?.next
hare = hare?.next?.next
if (tortoise === hare) {
return tortoise
}
}
return null
}
fun detectCycle(head: ListNode?): ListNode? {
if (head == null) {
return null
}
// If there is a cycle, the fast/slow pointers will intersect at some
// node. Otherwise, there is no cycle, so we cannot find an entrance to
// a cycle.
val intersect: ListNode = getIntersect(head) ?: return null
// To find the entrance to the cycle, we have two pointers traverse at
// the same speed -- one from the front of the list, and the other from
// the point of intersection.
var ptr1: ListNode = head
var ptr2: ListNode = intersect
while (ptr1 !== ptr2) {
ptr1 = ptr1.next
ptr2 = ptr2.next
}
return ptr1
}
}
PHP
Hash Table
/**
* Definition for a singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* public $val = 0;
* public $next = null;
* function __construct($val) { $this->val = $val; }
* }
*/
class Solution
{
/**
* @param ListNode $head
* @return ListNode
*/
function detectCycle($head)
{
$visited = [];
while (!is_null($head)) {
if (isset($visited[$head->val])) {
return $head;
}
$visited[$head->val] = true;
$head = $head->next;
}
return null;
}
}
Floyd's Tortoise and Hare
/**
* Definition for a singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* public $val = 0;
* public $next = null;
* function __construct($val) { $this->val = $val; }
* }
*/
class Solution
{
/**
* @param ListNode $head
* @return ListNode
*/
function detectCycle($head)
{
if (is_null($head)) {
return null;
}
$intersect = $this->getIntersect($head);
if (is_null($intersect)) {
return null;
}
$ptr1 = $head;
$ptr2 = $intersect;
while ($ptr1 !== $ptr2) {
$ptr1 = $ptr1->next;
$ptr2 = $ptr2->next;
}
return $ptr1;
}
private function getIntersect($head)
{
$tortoise = $head;
$hare = $head;
while (!is_null($hare) && !is_null($hare->next)) {
$tortoise = $tortoise->next;
$hare = $hare->next->next;
if ($tortoise === $hare) {
return $tortoise;
}
}
return null;
}
}
Python
Hash Table
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def detectCycle(self, head: ListNode | None) -> ListNode | None:
visited = set()
node = head
while node is not None:
if node in visited:
return node
visited.add(node)
node = node.next
return None
Floyd's Tortoise and Hare
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def getIntersect(self, head: ListNode | None) -> ListNode | None:
tortoise = head
hare = head
# A fast pointer will either loop around a cycle and meet the slow
# pointer or reach the `null` at the end of a non-cyclic list.
while hare is not None and hare.next is not None:
tortoise = tortoise.next
hare = hare.next.next
if tortoise == hare:
return tortoise
return None
def detectCycle(self, head: ListNode | None) -> ListNode | None:
if head is None:
return None
# If there is a cycle, the fast/slow pointers will intersect at some
# node. Otherwise, there is no cycle, so we cannot find an entrance to
# a cycle.
intersect = self.getIntersect(head)
if intersect is None:
return None
# To find the entrance to the cycle, we have two pointers traverse at
# the same speed -- one from the front of the list, and the other from
# the point of intersection.
ptr1 = head
ptr2 = intersect
while ptr1 != ptr2:
ptr1 = ptr1.next
ptr2 = ptr2.next
return ptr1
Rust
Swift
Hash Table
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public var val: Int
* public var next: ListNode?
* public init(_ val: Int) {
* self.val = val
* self.next = nil
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
func detectCycle(_ head: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
var visited = [ListNode]()
var node = head
while node != nil {
if visited.contains(where: {$0 === node!}) {
return node
}
visited.append(node!)
node = node?.next
}
return nil
}
}
Floyd's Tortoise and Hare
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public var val: Int
* public var next: ListNode?
* public init(_ val: Int) {
* self.val = val
* self.next = nil
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private func getIntersect(_ head: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
var hare = head, tortoise = head
while hare != nil, hare?.next != nil {
tortoise = tortoise?.next
hare = hare?.next?.next
if tortoise === hare {
return tortoise
}
}
return nil
}
func detectCycle(_ head: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
if head == nil {
return nil
}
let intersect = getIntersect(head)
if intersect == nil {
return nil
}
var ptr1 = head
var ptr2 = intersect
while ptr1 !== ptr2 {
ptr1 = ptr1?.next
ptr2 = ptr2?.next
}
return ptr1
}
}
