230. Kth Smallest Element in a BST
題目敘述
Given the root of a binary search tree, and an integer k, return the k**th smallest value (1-indexed) of all the values of the nodes in the tree.
Example 1:
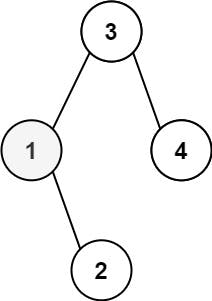
Input: root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1
Output: 1
Example 2:
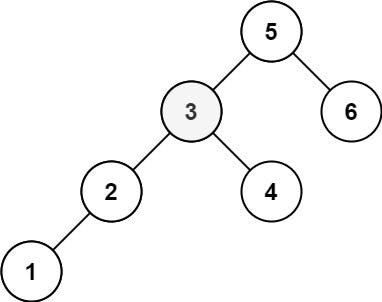
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], k = 3
Output: 3
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is
n. 1 <= k <= n <= 10**40 <= Node.val <= 10**4
Follow up: If the BST is modified often (i.e., we can do insert and delete operations) and you need to find the kth smallest frequently, how would you optimize?
Hint 1:
Try to utilize the property of a BST.
Hint 2:
Try in-order traversal.
Hint 3:
What if you could modify the BST node's structure?
Hint 4:
The optimal runtime complexity is O(height of BST).
題目翻譯
這題目是要在一個二元搜尋樹中,第 k 個最小的數值。
解法解析
這題目算是已經可以大概知道就是有 Iteration 和 Recursion 的兩種解法。而且利用二元樹的特性,因為左側是最小值,直接先從最左側開始往回找。
解法範例
Go
Iteration
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func kthSmallest(root *TreeNode, k int) int {
stack := []*TreeNode{}
cur := root
for k >= 0 {
for cur != nil {
stack = append(stack, cur)
cur = cur.Left
}
cur = stack[len(stack)-1]
stack = stack[:len(stack)-1]
k--
if k == 0 {
return cur.Val
}
cur = cur.Right
}
return cur.Val
}
Recursion
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func kthSmallest(root *TreeNode, k int) int {
cur := 0
val := 0
dfs(root, k, &cur, &val)
return val
}
func dfs(node *TreeNode, k int, cur, val *int) {
if node == nil {
return
}
dfs(node.Left, k, cur, val)
*cur = *cur + 1
if *cur == k {
*val = node.Val
}
dfs(node.Right, k, cur, val)
}
JavaScript
Iteration
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} k
* @return {number}
*/
var kthSmallest = function (root, k) {
const stack = [];
let cur = root;
while (cur || stack.length) {
while (cur) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
cur = stack.pop();
k--;
if (!k) {
return cur.val;
}
cur = cur.right;
}
};
Recursion
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} k
* @return {number}
*/
var kthSmallest = function (root, k) {
let answer = 0;
function inorder(root) {
if (!root) return;
inorder(root.left);
if (--k === 0) {
answer = root.val;
return;
}
inorder(root.right);
}
inorder(root);
return answer;
};
Kotlin
PHP
Python
Iteration
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def kthSmallest(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], k: int) -> int:
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type k: int
:rtype: int
"""
stack = []
while True:
while root:
stack.append(root)
root = root.left
root = stack.pop()
k -= 1
if not k:
return root.val
root = root.right
Recursion
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def kthSmallest(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], k: int) -> int:
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type k: int
:rtype: int
"""
def inorder(r):
return inorder(r.left) + [r.val] + inorder(r.right) if r else []
return inorder(root)[k - 1]
Rust
Swift